这不是教程,只是个人总结,有兴趣的童鞋可以搭配源码看看:acuprpc
微服务除了在内部相互调用,有时某些服务也会提供给外部应用。当然不能让外部应用也加入到“大家庭”里,毕竟知人知面不知源码,我们可以派出一个“前台”去接待它们,这就是“网关”。
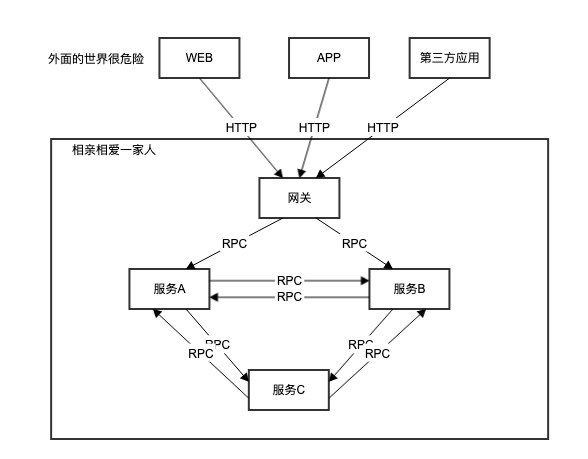
网关负责对接外部来宾,因此要做好安全措施,什么登陆、权限该上就上。
流程如下:
- 网关收到请求
- 解析请求(服务名,方法,参数等)
- 选择一个实例(来自注册中心)
- RPC调用
- 结果返回给请求方
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
private RpcClientManager rpcClientManager;
public ApiController(RpcClientManager rpcClientManager) {
this.rpcClientManager = rpcClientManager;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json")
public Object invoke(@RequestBody RpcRequestDTO requestDTO) {
RpcServiceInfo serviceInfo = new RpcServiceInfo(requestDTO.getApp(), requestDTO.getService());
RpcClient client = rpcClientManager.lookup(serviceInfo);
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest(requestDTO.getApp(), requestDTO.getService(), requestDTO.getMethod());
if (requestDTO.getParameters() != null) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
requestDTO.getParameters().forEach((k, v) -> map.put(k, JsonUtil.toJson(v)));
request.setNamedParameter(map);
}
return client.invoke(request);
}
}
|
这个demo作为一个子模块(acuprpc-spring-boot-starter-gateway)加入了框架的全家桶,直接引入依赖就能使用这个功能。
基于这个方法,可以实现更加复杂的也无需求,这里就不细讲了,本系列结束。
